Cranial nerves NCS
|
Nerve |
Active |
Reference |
Ground |
Stimulation |
Lat Max (Onset) |
Amp. (Min) |
|
|
Facial
nerve
|
Nasalis, on the lateral mid-nose.
The subject may “wrinkle the nose” and the electrode is placed on the most
prominent bulge of the muscle. Orbicularis oculi under the eye
in line with the pupil. An alternate position is at the lateral border of the
eye. Orbicularis oris
lateral to the angle of the mouth |
on the tip or bridge of the nose |
over the base of the neck or on
the cheek |
Preauricular stimulation is
performed with the cathode just anterior to the lower ear over the substance
of the parotid gland and several centimeters superior to the angle of the
mandible. Postauricular stimulation is
performed by placing the cathode just behind the lower ear, below the mastoid
process and behind the neck of the mandible. The anode is posterior |
3.5 3.8 |
>50% difference is significant >90% indicate surgery |
|
|
Cranial
accessory
|
Over the upper trapezius, about 9 cm lateral to the 7th
spinous process. |
3 cm lateral to the active electrode. |
between the stimulating and recording electrodes |
In the posterior triangle of the neck, 1–2 cm posterior to
the posterior border sternocleidomastoid muscle and slightly above the
midpoint of this muscle. This is a point halfway between the mastoid process
and the suprasternal notch. The anode is superior |
3 |
3 |
|
|
Great
auricular nerve
|
On the back of the ear lobe |
2 cm above the active electrode |
On the back of the neck. |
8 cm from the active electrode
along the lateral border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, with the cathode
superior |
1.6 |
|
|
|
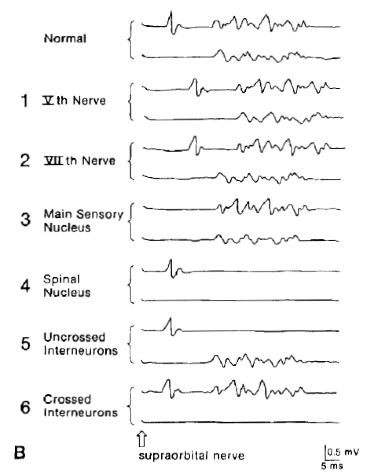
Blink
reflex
|
Over the lower lateral orbicularis oculi muscle
bilaterally |
Over the temple or the lateral surface of the nose above
the nasalis muscle |
Under the chin or on the forehead or cheek |
Cathode (C) over the supraorbital nerve at the
supraorbital notch. The anode is superolateral. A ratio of R1 latency (R) to the direct response latency
(D) can be calculated. This R/D ratio should not fall outside the range of
2.6 to 4.6. A larger ratio, with a normal D, is indicative of slowing
of the trigeminal portion. If the R/D ratio is low, it is indicative of
slowing of the facial nerve. A glabellar tap with a special hammer can be used instead
of electrical stimulation |
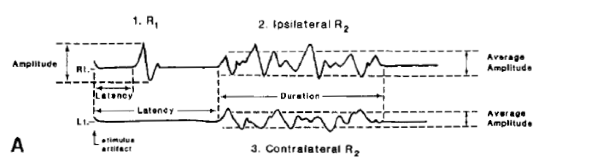
Direct latency: 4 Ipsilateral R1: 13 Ipsilateral R2: 40 Contralat R2: 41 Several blink responses should be tested and the shortest
latencies chosen. Latency should be measured to the first deflection from
the baseline |
|
|