Lower limb Motor NCS
|
Nerve |
Origin |
Active |
Reference |
Ground |
Stimulation |
Lat. (Max) |
Amp. (Min) |
NCV (Min) |
F Lat. (Max) |
|
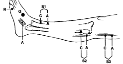
Femoral
to Quadriceps |
L2,3,4 |
Center of vastus medialis |
Quadriceps tendon near the
patella |
Between active & reference
electrode |
Needle electrode is used. A- Superior to the inguinal
ligament just lateral to the femoral artery. B- Inferior to the inguinal
ligament and lateral to the femoral artery. |
8.5 7.5 |
0.5 |
|
|
|
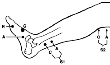
Peroneal to Ext Dig Brevis |
L5,S1 |
On extensor digitorum brevis muscle on the dorsum of the
foot. |
5th MCP |
Between active & reference electrode |
A- 8 cm proximal to the active electrode, slightly lateral
to the tibialis anterior tendon B- Posterior and inferior to the fibular head. |
6.5 |
1.2 |
40 |
60 |
|
Tibial to Abductor Hallucis
|
S1,S2 |
Medial foot,
slightly anterior and inferior to the navicular tubercle (at the most
superior point of the arch |
1st MCP |
Between active & reference
electrode |
A- posterior to the medial
malleolus B- Mid-popliteal fossa |
6 |
4 |
40 |
60 |
|
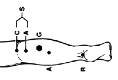
Tibial
to Flex Dig Min Brevis
|
S1,S2 |
Midpoint of inferolateral edge of 5th
metatarsal. |
5th MCP |
Between active & reference electrode |
Posterior to the medial malleolus |
8 |
1.2 |
|
|
|
H reflex to Calf muscle
|
S1 |
On the back of leg, Midpoint
between popliteal crease and posterior calcaneus. |
Posterior calcaneus |
Between active & reference
electrode |
Mid-popliteal crease with the anode distal |
35 |
|
|
|
An accessory peroneal nerve is commonly present (20–25%
incidence). The accessory peroneal nerve passes behind the lateral malleolus to
innervate the extensor digitorum brevis. Its presence should be suspected if
the amplitude to proximal stimulation is greater than on ankle stimulation. Its
presence can be confirmed by stimulating behind the lateral malleolus. If a
response is recorded from the extensor digitorum brevis, an accessory peroneal
nerve is present